

outermost gas layers of galaxies in nearby and/or low-mass galaxy clusters. Ram pressure may also have facilitated strangulation through the removal of galactic coronal gas. Ram-pressure stripping by the gaseous intracluster medium has been proposed. through turbulent viscous stripping is comparable to the mass of hot ICM material. While these processes are generally insufficient to explain observed H i deficiencies, they could still be important for H i removal in the X-ray bright groups, potentially removing more than half of the interstellar medium in the X-ray bright HCG 97. As a mechanism, ram pressure should predict a correlation with p, V2. First, dwarf galaxies with lower mass that have lower restoring force can be stripped.
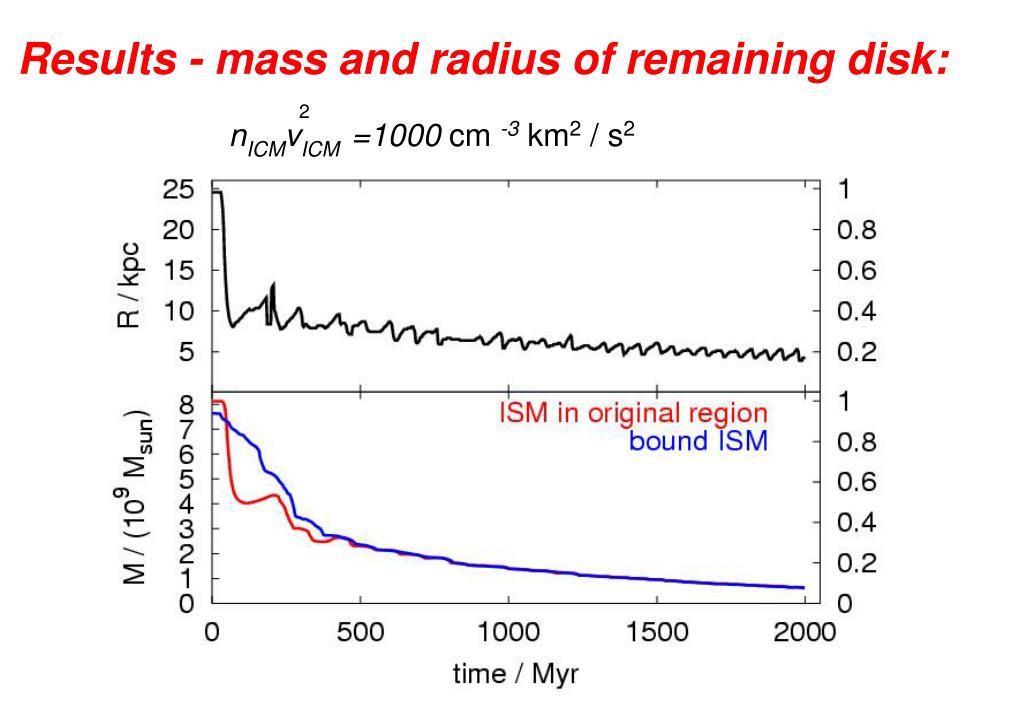
Combining the inferred IGM distributions with analytical models of representative disc galaxies orbiting within each group, we estimate the H i mass-loss due to ram-pressure and viscous stripping. We take an analytical approach to study ram pressure stripping. The observations of shrunken HI disks with respect to optical disks and asymmetric HI distributions are consistent with ram pressure stripping. No clear evidence is seen for any of the members being currently stripped of any hot gas, nor for galaxies to show enhanced nuclear X-ray activity in the X-ray bright or most H i deficient groups. Based on the simulation, we discuss a possible history of interstellar gas in M31 system, which comprises M32, NGC 205 and possible merged galaxies. falling into a cluster experience ram pressure from dense intracluster medium (ICM) gas that can potentially unbind their individual gas reservoirs (Gunn et al. Diffuse X-ray emission associated with an IGM is detected in four of the groups, suggesting that galaxy–IGM interactions are not the dominant mechanism driving cold gas out of the group members. The ram-pressure process is significant durig merger of galaxies, in which interstellar gas is stripped and accreted prior to the stellar-body merger. In order to investigate the role played by a hot intragroup medium (IGM) for the removal and destruction of H i in these systems, we have performed a Chandra and XMM–Newton study of eight of the most H i deficient Hickson compact groups. Galaxies in compact groups tend to be deficient in neutral hydrogen compared to isolated galaxies of similar optical properties.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
